Ecological succession examples
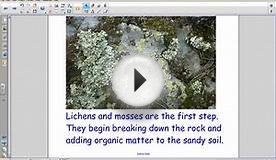
The first species to arrive either after a disturbance, such as a flood, or when the land is first formed, such as a new volcanic island, are called pioneer species. They are the first colonizers. Grasses, mosses, lichens, and other plants are pioneer species. Pioneer species may even be able to survive without soil. These pioneer species are often quite hardy and are thus able to survive in a harsh environment. Pioneer species also typically have light seeds that disperse easily through wind.
As these pioneer plants live, attract consumers, and die, soil is either formed or improved to the point where other plants will begin to grow. As these new species reach and spread across the environment, it is no longer suitable for pioneer species, which will eventually disappear or compose a minimal part of the community.
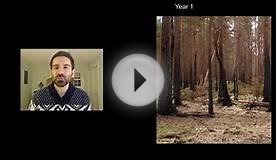
Herbs and then shrubs will eventually arrive and finally trees. Below is an example of ecological succession of a boreal forest.

A community may eventually reach its climax, the point where the composition remains mostly stable unless some sort of disturbance occurs. The community would then be called a climax community.
|
Is your lunch causing global warming? Cars and factories are major sources of greenhouse gas emissions that are heating up the planet. But what you ... An article from: New York Times Upfront Book (Scholastic, Inc.) |

|
Wallmonkeys Ecological Footprint Symbol Peel and Stick Wall Decals (24 in W x 16 in H) Home (Wallmonkeys)
|