Stages of ecological succession
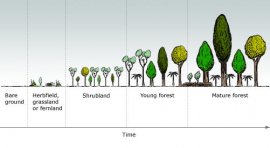 During a succession, different groups of plants grow at a site over time. The diagram shows a succession from bare ground to a mature forest.
During a succession, different groups of plants grow at a site over time. The diagram shows a succession from bare ground to a mature forest.
Plants that colonise bare ground are typically hardy and low-growing. In time, shrubs and small trees grow among the first plants, and a shrubland develops. Seedlings of tall forest trees germinate and grow in the shelter of the shrubs, and soon overtop them, forming a young forest. This gets taller and more complex over time. In the mature forest, individual trees die and young saplings grow up to replace them, but the forest’s composition and structure basically remain the same for centuries.
About this item
Te Ara - The Encyclopedia of New Zealand
Artwork by Gareth Railton
This item has been provided for private study purposes (such as school projects, family and local history research) and any published reproduction (print or electronic) may infringe copyright law. It is the responsibility of the user of any material to obtain clearance from the copyright holder.
How to cite this page:
Maggy Wassilieff. 'Forest succession and regeneration - Forest succession', Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand, updated 8-Jul-13



|
iPhone 5 case iPhone 5S Case EcologicolSuccessien EcologicolSuccessien Images Redorbit Ecological Processes beautiful design cover case. Wireless (Yeclon)
|