Greenhouse effect global warming climate change
Global Emissions by Gas
At the global scale, the key greenhouse gases emitted by human activities are:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) - Fossil fuel use is the primary source of CO2. The way in which people use land is also an important source of CO2, especially when it involves deforestation. Land can also remove CO2 from the atmosphere through reforestation, improvement of soils, and other activities.
- Methane (CH4) - Agricultural activities, waste management, and energy use all contribute to CH4 emissions.
- Nitrous oxide (N2O) - Agricultural activities, such as fertilizer use, are the primary source of N2O emissions.
- Fluorinated gases (F-gases) - Industrial processes, refrigeration, and the use of a variety of consumer products contribute to emissions of F-gases, which include hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
Black carbon (BC) is a solid particle or aerosol, not a gas, but it also contributes to warming of the atmosphere. Learn more about BC and climate change on our Causes of Climate Change page.
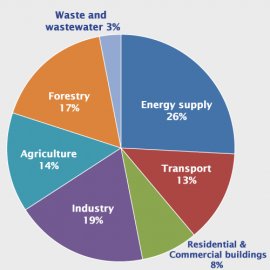
Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Source
Source: IPCC (2007);based on global emissions from 2004. Details about the sources included in these estimates can be found in the Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change .
Global Emissions by Source
Global greenhouse gas emissions can also be broken down by the economic activities that lead to their production.


 Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The mechanism is that bodies with a temperature above absolute zero have atoms or molecules with kinetic energies which are changing, and these changes...
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The mechanism is that bodies with a temperature above absolute zero have atoms or molecules with kinetic energies which are changing, and these changes...