Effect of CO2 on global warming
 Global warming is primarily a problem of too much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This carbon overload is caused mainly when we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas or cut down and burn forests. There are many heat-trapping gases (from methane to water vapor), but CO2 puts us at the greatest risk of irreversible changes if it continues to accumulate unabated in the atmosphere. There are two key reasons why.
Global warming is primarily a problem of too much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This carbon overload is caused mainly when we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas or cut down and burn forests. There are many heat-trapping gases (from methane to water vapor), but CO2 puts us at the greatest risk of irreversible changes if it continues to accumulate unabated in the atmosphere. There are two key reasons why.
CO2 has caused most of the warming and its influence is expected to continue
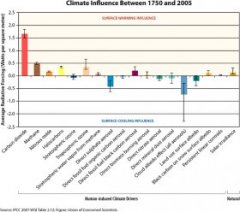
CO2, more than any other cf driver, has contributed the most to climate change between 1750 and 2005.[1, 2, 3] The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) issued a global climate assessment in 2007 that compared the relative influence exerted by key heat-trapping gases, tiny particles known as aerosols, and land use change of human origin on our climate between 1750 and 2005.[3] By measuring the abundance of heat-trapping gases in ice cores, the atmosphere, and other climate drivers along with models, the IPCC calculated the “radiative forcing” (RF) of each climate driver—in other words, the net increase (or decrease) in the amount of energy reaching Earth’s surface attributable to that climate driver. Positive RF values represent average surface warming and negative values represent average surface cooling. CO2 has the highest positive RF (see Figure 1) of all the human-influenced climate drivers compared by the IPCC. Other gases have more potent heat-trapping ability molecule per molecule than CO2 (e.g. methane), but are simply far less abundant in the atmosphere and being added more slowly.
 Figure 1. How Does CO2 Compare To Other Climate Drivers?
Figure 1. How Does CO2 Compare To Other Climate Drivers?
Carbon dioxide (CO2), more than any other climate driver, has contributed the most to climate change between 1750 and 2005.[4]
CO2 sticks around
CO2 remains in the atmosphere longer than the other major heat-trapping gases emitted as a result of human activities. It takes about a decade for methane (CH4) emissions to leave the atmosphere (it converts into CO2) and about a century for nitrous oxide (N2O).[3] In the case of CO2, much of today’s emissions will be gone in a century, but about 20 percent will still exist in the atmosphere approximately 800 years from now.[3] This literally means that the heat-trapping emissions we release today from our cars and power plants are setting the climate our children and grandchildren will inherit. CO2’s long life in the atmosphere provides the clearest possible rationale for reducing our CO2 emissions without delay.
What about water vapor?
Water vapor is the most abundant heat-trapping gas, but rarely discussed when considering human-induced climate change. The principal reason is that water vapor has a short cycle in the atmosphere (a few days) before it is incorporated into weather events and falls to Earth, so it cannot build up in the atmosphere in the same way as carbon dioxide does.[1, 2]

